The Mughal Empire was one of the most powerful and influential empires in Indian history. It ruled large parts of the Indian subcontinent from the early 16th century to the mid-19th century. Known for its strong administration, impressive monuments, and rich culture, the Mughal Empire left a lasting impact on Indian society, art, and governance.
Mughal Empire: Key Details
In almost every competitive exam where History is asked in the General Awareness section, The Mughal Empire is one of the most asked and repeated topics. So it becomes necessary for the candidates preparing for such exams to have a basic idea regarding the same. The key details of the Mughal Dynasty including the time period, language, religion, capital, etc. are tabulated below.
| Name | Mughal Dynasty Or Mughal Empire |
|---|---|
| Period | 1526- 1857 AD. |
| Common Language | Persian (Official and court language), Urdu (later given official status), Chagatai (spoken in the initial years), Arabic (for religious ceremonies) and other Indian languages |
| Religion | Sunni Islam (Hanafi) (1526-1857), Din-i Ilahi (1582-1605) |
| Capital |
|
| Government | Unitary absolute monarchy under a federal structure
|
| Currency | Rupee, Taka and Dam |
History of Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire began in 1526 when Babur defeated the Sultan of Delhi, Ibrahim Lodi, at the First Battle of Panipat. Over the next three centuries, the Mughals expanded their control over a large part of India. The empire reached its height under Akbar, Jahangir, Shah Jahan, and Aurangzeb. However, it started to decline after Aurangzeb’s death in 1707 due to weak successors, internal problems, and rising European powers, especially the British.
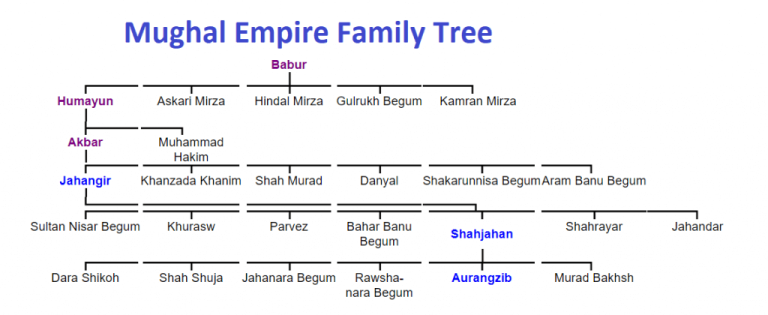
Mughal Empire Family Tree
The Mughal emperors came from a royal line that traced its roots to two legendary rulers: Timur (from Central Asia) and Genghis Khan (from Mongolia). This gave them a strong claim to power and a mix of cultures from both East and West Asia.
Mughal Family Lineage Table
| Emperor | Reign | Relation |
|---|---|---|
| Babur | 1526–1530 | Founder of the Empire |
| Humayun | 1530–1540, 1555–1556 | Son of Babur |
| Akbar | 1556–1605 | Son of Humayun |
| Jahangir | 1605–1627 | Son of Akbar |
| Shah Jahan | 1627–1658 | Son of Jahangir |
| Aurangzeb | 1658–1707 | Son of Shah Jahan |
| Later Emperors | 1707–1857 | Descendants of Aurangzeb |
Mughal Emperors
The Mughal Dynasty was established by Babur and the last ruler of the dynasty was Bahadur Shah Zafar II. The power after the Mughal Empire was transferred to the hands of the British. Here we provide you a complete list of Mughal Emperors, which is very helpful in making notes for your exam preparation.
| Titular Name | Birth Name | Birth | Reign | Death |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Babur | Zahir al-Din Muhammad | 14 February 1483 Andijan, Uzbekistan | 20 April 1526 – 26 December 1530 | 26 December 1530 (aged 47) Agra, India |
| Humayun | Nasir al-Din Muhammad | 6 March 1508 Kabul, Afghanistan | 26 December 1530 – 17 May 154022 February 1555 – 27 January 1556
(10 years 3 months 25 days) |
27 January 1556 (aged 47) Delhi, India |
| Akbar the Great | Jalal al-Din Muhammad | 15 October 1542 Umerkot, Pakistan | 11 February 1556 – 27 October 1605(49 years 9 months 0 days) | 27 October 1605 (aged 63) Agra, India |
| Jahangir | Nur al-Din Muhammad | 31 August 1569 Agra, India | 3 November 1605 – 28 October 1627(21 years 11 months 23 days) | 28 October 1627 (aged 58) Jammu and Kashmir, India |
| Shah Jahah | Shihab al-Din Muhammad | 5 January 1592 Lahore, Pakistan | 19 January 1628 – 31 July 1658(30 years 8 months 25 days) | 22 January 1666 (aged 74) Agra, India |
| Aurangzeb Alamgir | Muhi al-Din Muhammad | 3 November 1618 Gujarat, India | 31 July 1658 – 3 March 1707(48 years 7 months 0 days) | 3 March 1707 (aged 88) Ahmednagar, India |
| Azam Shah | Qutb al-Din Muhammad | 28 June 1653 Burhanpur, India | 14 March 1707 – 20 June 1707 | 20 June 1707 (aged 53) Agra, India |
| Bahadur Shah | Qutb al-Din Muhamma | 14 October 1643 Burhanpur, India | 19 June 1707 – 27 February 1712(4 years, 253 days) | 27 February 1712 (aged 68) Lahore, Pakistan |
| Jahandar Shah | Muiz al-Din Muhammad | 9 May 1661 Deccan, India | 27 February 1712 – 11 February 1713(0 years, 350 days) | 12 February 1713 (aged 51) Delhi, India |
| Farrukh Siyar | Muin al-Din Muhammad Puppet King under the Sayyids of Barha |
20 August 1685 Aurangabad, India | 11 January 1713 – 28 February 1719(6 years, 48 days) | 19 April 1719 (aged 33) Delhi, India |
| Rafi ud-Darajat | Shams al-Din Muhammad Puppet King under the Sayyids of Barha |
1 December 1699 | 28 February 1719 – 6 June 1719(0 years, 98 days) | 6 June 1719 (aged 19) Agra, India |
| Shah Jahan II | Rafi al-Din Muhammad Puppet King under the Sayyids of Barha | 5 January 1696 | 6 June 1719 – 17 September 1719(0 years, 105 days) | 18 September 1719 (aged 23) Agra, India |
| Muhammad Shah | Nasir al-Din Muhammad Puppet King under the Sayyids of Barha | 7 August 1702 Ghazni, Afghanistan | 27 September 1719 – 26 April 1748(28 years, 212 days) | 26 April 1748 (aged 45) Delhi, India |
| Ahmad Shah Bahadur | Mujahid al-Din Muhammad | 23 December 1725 Delhi, India | 29 April 1748 – 2 June 1754(6 years, 37 days) | 1 January 1775 (aged 49) Delhi, India |
| Alamgir II | Aziz al-Din Muhammad | 6 June 1699 Burhanpur, India | 3 June 1754 – 29 November 1759(5 years, 180 days) | 29 November 1759 (aged 60) Kotla Fateh Shah, India |
| Shah Jahan III | Muhi al-Millat | 1711 | 10 December 1759 – 10 October 1760(282 days) | 1772 (aged 60–61) |
| Shah Alam II | Jalal al-Din Muhammad Ali Gauhar | 25 June 1728 Delhi, India | 10 October 1760 – 31 July 1788(27 years, 301 days) | 19 November 1806 (aged 78) Delhi, India |
| Shah Jahan IV | Bidar Bakht Mahmud Shah Bahadur Jahan Shah | 1749 Delhi, India | 31 July 1788 – 11 October 1788(63 days) | 1790 (aged 40–41) Delhi, India |
| Shah Alam II | Jalal al-Din Muhammad Ali Gauhar, Puppet King under the Maratha Empire | 25 June 1728 Delhi, India | 16 October 1788 – 19 November 1806(18 years, 339 days) | 19 November 1806 (aged 78) Delhi, India |
| Akbar Shah II | Muin al-Din Muhammad, Puppet King under the East India Company | 22 April 1760 Mukundpur, India | 19 November 1806 – 28 September 1837(30 years, 321 days) | 28 September 1837 (aged 77) Delhi, India |
| Bahadur Shah II Zafar | Abu Zafar Siraj al-Din Muhammad | 24 October 1775 Delhi, India | 28 September 1837 – 21 September 1857(19 years, 360 days) | 7 November 1862 (aged 87) Rangoon, Myanmar |
Rise of the Mughal Empire
Babur, originally a ruler from Central Asia, came to India to expand his territory. After defeating Ibrahim Lodi at Panipat, he set up the foundation of the Mughal Empire. His successors, especially Akbar, strengthened and expanded the empire with smart policies, military power, and alliances. Akbar’s rule is especially remembered for bringing together people of different religions and cultures.
Major Mughal Emperors
The Mughal Empire had several notable rulers who contributed to its glory:
Babur (1526–1530)
- Babur was born in 1483 in Fargana(Afganistan).
- He was the founder of the Mughal Empire, who introduced gunpowder in India.
- Babur defeated Ibrahim Lodhi in the First Battle of Panipat (AD 1526)
- Defeated Rana Sanga (Sangram Singh) at the Battle of Khanwa (AD 1527)
- Defeated Medini Rai of Chanderi at the Battle of Chanderi (AD 1528)
- Defeated Mahmud Lodi at the Battle of Ghagra (AD 1529). This was the last Battle fought by Babur.
- He wrote Tuzuk-i-Baburi (Autobiography of Babur) in the Turkish language.
- Babur declared Jehad and adopted the title, Ghazi(After the Khanva War)
- According to Tuzuk-i-Baburi, Babur Died in 1530 in Lahore and was buried at Aram Bagh (Agra). Later his body was taken to Afghanistan (Kabul).
Humayun (AD 1530-1556)
- Humayun was born on March 6, 1508, in Kabul, Afghanistan.
- Humayun was the eldest son of Babur. He ascended to the throne of the Mughal Empire in 1530 after the death of his father.
- Built Dinpanah in Delhi as his second capital.
- Sher Shah Suri gradually gained power. He fought two battles with Humayun – The battle of Chausa (AD 1539) and another Battle of Kannauj (AD 1540) culminating in Humayun’s defeat.
- Humayun spent 15 years in exile. He again invaded India in 1555 with the help of his officer Bairam Khan.
- Humayun died in AD 1556 due to a fall from his library building’s stairs.
- Gulbadan Begum, Humayun’s half-sister wrote Humayun-Nama.
Humayun Biography, Second Mughal Empire (Click here to Check)
Akbar (AD 1556-1605)
- Abu’l-Fath Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar popularly known as Akbar succeeded Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expand and consolidate Mughal domains in India.
- Considered to be one of the greatest rulers of all time.
- Defeated Hemu at the Second Battle of Panipat (AD 1556) with the help of Bairam Khan
- Conquered Malwa (AD 1561) defeating Baz Bahadur followed by Garh-Katanga (ruled by Rani Durgawati), Chittor (AD 1568), Ranthambhor, and Kalinjar (AD 1569), Gujarat (AD 1572), Mewar (Battle of Haldighati, AD 1576 Akbar and Rana Pratap), Kashmir (AD 1586), Sindh (AD 1593) and Asirgarh (AD 1603).
- Buland Darwaza was constructed at Fatehpur Sikri after its victory over Gujarat in AD 1572.
- Akbar married Harka Bai (also known as Jodha Bai), the daughter of Rajput ruler Bharmal.
- Akbar abolished Jaziyah (AD 1564).
- He believed in Sulh-i-Kul (peace to all), built Ibadat Khana (Hall of prayer) at Fatehpur Sikri; issued ‘Degree of Infallibility (AD 1579); formulated religious order Din-i-Ilahi (AD 1582). Birbal was the first to embrace it.
- The land revenue system was called the Todar Mal Bandobast or Zabti System measurement of land, classification of land, and fixation of rent; and introduced the Mansabdari System (holder of rank) to organize nobility and army.
- The Navratnas included Todar Mal, Abul Fazal, Faizi, Birbal, Tansen, Abdur Rahim Khana-i-Khana, Mullah-do-Pyaza, Raja Man Singh and Fakir Aziao-Din.
- Akbar died on 27 October 1605 due to dysentery. His body was buried at his mausoleum in Sikandra, Agra.
Jahangir (AD 1605-1627)
- During Jahangir’s rule, the British East India Company was granted trading rights in India.
- Executed the fifth Sikh guru, Guru Arjun Dev.
- His greatest failure was the loss of Kandahar to Persia in AD 1622.
- Jahangir married Mehr-un-Nisa in AD 1611 and conferred the title of Nurjahan on her.
- He established Zanjir-i-Adal at Agra Fort for the seekers of royal justice.
- Captain Hawkins and Sir Thomas Roe visited his court.
- In the later years of his rule, Jahangir’s health declined, and his son Khurram (Shah Jahan) effectively took over the administration.
- Jahangir passed away on October 28, 1627, in Rajauri, while on his way to Kashmir.
Shahjahan (AD 1628-1658)
- Shahjahan had an insatiable passion for building
- Under his rule, the Taj Mahal of Agra and the Jama Masjid of Delhi, among other monuments, were erected.
- His reign marked the cultural zenith of Mughal rule.
- His military expeditions brought the empire to the brink of bankruptcy.
- His sons commanded large armies on different fronts.
- During his reign, the Marwari horse was introduced.
- The Taj Mahal, the eternal love monument is located in Agra. Shah Jahan commissioned its construction as a mausoleum for his favorite wife, Arjumancl Bano Begum, better known as Mumtaz Mahal, in 1631.
- A rebellion of the Sikhs led by Guru Hargobind took place. Shah Jahan ordered the destruction of the Sikh temple in Lahore.
Aurangzeb (Alamgir) (AD 1658-1707)
- Aurangzeb was the son of Mumtaz and Shahjahan.
- Aurangzeb became victorious after the brutal war of succession between his brothers Dara, Shuja, and Murad.
- Rebellions during his rule – Jat Peasantry at Mathura, Satnami peasantry in Punjab, and Bundelas in Bundelkhand.
- The annexation of Marwar in AD 1658 led to a serious rift between the Rajput and Mughals after the death of Raja Jaswant Singh.
- The ninth Sikh Guru, Guru Tegh Bahadur was executed by him in AD 1675.
- Mughal conquests reached a territorial climax during his reign.
- It stretched from Kashmir in the North to Jinji in the South, from the Hindukush in the West to Chittagong in the East.
- He was called Darvesh or Zinda Pir. He forbade Sati. Conquered Bijapur (AD 1686) and Golconda (AD 1687) and reimposed Jaziya in AD 1679.
- He built Biwi ka Makbara on the tomb of his queen Rabaud-Durrani at Aurangabad; Moti Masjid within Red Fort, Delhi; and the Jami or Badshahi Mosque at Lahore.
- Aurangzeb died in 1707 in Ahmednagar.
Other Mughal Rulers
After the death of Aurangzeb, there was a clear decline in the Mughal’s command over the empire. However, there were some rulers who tried to restore the glory of the empire. Some historians have called this period the time of the ‘Later Mughals’. Let us have a look at the next stage of the Mughal Empire
Bahadur Shah I (1707-12)
- The original name was Muazzam
- Title, Shah-e-Bekhabar.
- Promote a friendly relationship with Marathas and Rajputs
Jahandar Shah (1712-13)
- He ascended the throne with the help of Zulfikar Khan (Wazir).
- Abolished Jijiya.
- A Prostitute “LAL KUAR” dominated his court
Farrukhsiyar (1713-19)
- He lacked the ability and knowledge to rule independently.
- His reign saw the emergence of the Sayyid Brothers (known as kingmakers).
- Abdulla Khan-Wazir
- Hussain Ali-Senapati
- 1717-Issued Golden Farman to East India Company for free trade
- Farrukhsiyar executed Banda Bahadur ( A Sikh leader)
Muhammad Shah (1719-48)
- Became the emperor with the help of the Saiyad Brothers
- Nadir Shah invaded India and took away the Peacock throne and Kohinoor diamond.
- Title- Rangeela
- The emergence of the independent state in his period
Ahmed Shah (1748-54)
- Ahmed Shah Abdali (General of Nadir Shah) marched towards Delhi and the Mughals ceded Punjab and Multan.
- He worked under the guidance of Rajmata “Udam Bai”
Alamgir (1754-59)
- Ahmed Shah occupied Delhi Later, Delhi was plundered by Marathas.
Shah Alam II (1759-1806)
- Original NAME: Aligohar
- Panipat War: (1761)
- Buxar War (1764)
- Treaty of Allahabad (1765)
- Could not enter Delhi for 12 years.
- 1788: Gulam Kadir make him blind
Akbar II (1806-37)
- Pensioner of East India Company.
- Gave the title “Raja” to Ram Mohan Roy
Bahadur Shah II (1837-57)
- Nickname: Jafar
- The last Mughal Emperor was made premier during the 1857 Revolt.
- 1862-death in Rangoon (Myanmar)
Battles Fought by the Mughal Emperors
Throughout their rule, the Mughals fought many important battles. Some were for expansion, others to defend their throne.
List of Major Battles:
- First Battle of Panipat (1526) – Babur defeated Ibrahim Lodi, beginning Mughal rule.
- Battle of Khanwa (1527) – Babur defeated Rana Sanga of Mewar.
- Battle of Chanderi (1528) – Babur defeated Medini Rai.
- Battle of Ghaghra (1529) – Babur vs Afghan chiefs and the Sultan of Bengal.
- Battle of Kannauj (1540) – Sher Shah Suri defeated Humayun.
- Second Battle of Panipat (1556) – Akbar’s regent Bairam Khan defeated Hemu.
- Battle of Haldighati (1576) – Akbar’s army defeated Maharana Pratap.
- Deccan Campaigns (1600s) – Aurangzeb fought various southern kingdoms.
- Siege of Golconda (1687) – Aurangzeb annexed the rich Golconda kingdom.
Capitals of the Mughal Dynasty
The Mughals changed their capital cities several times, depending on political and strategic needs.
| Capital | Years | Ruler(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Agra | 1526 – 1556 | Babur, Humayun, Akbar (briefly) |
| Delhi | 1556 – late 17th century | Akbar, Jahangir, Shah Jahan, Aurangzeb |
| Fatehpur Sikri | 1571 – 1585 | Akbar |
| Lahore | 1585 – 1598 | Akbar |
| Shahjahanabad (Old Delhi) | 1639 – 1857 | Shah Jahan, Aurangzeb (briefly) |
| Agra (again) | Late 17th century | Aurangzeb |
| Aurangabad | 17th century | Aurangzeb |
Key Features of Mughal Empire
Administrative System of Mughals
The Mughal Empire had a well-organized administration that helped it run such a vast territory efficiently.
Key Features:
- Centralized government led by the emperor.
- Provinces called “Subas” were managed by governors.
- Revenue collection based on land measurement.
- Officials ranked using the Mansabdari system.
Table of Administrative Structure
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Suba | Province |
| Subedar | Governor of a Suba |
| Mansab | Rank of an official |
| Jagir | Land grant given to officials |
| Diwan | Finance officer |
Economy
The Mughal economy was mainly based on agriculture. Taxes were collected in cash or kind from farmers. Trade flourished within India and with other countries. India was famous for its textiles, especially cotton and silk, and spices. Important trade routes connected India with Persia, Central Asia, and Europe. Ports like Surat and Masulipatnam played a key role in overseas trade.
Art and Literature
Mughal rule was a golden age for literature and art. Persian was the court language, and many historical texts, poems, and stories were written. Akbar had texts like the Ramayana and Mahabharata translated into Persian.
Famous writers:
- Abul Fazl – Wrote Akbarnama and Ain-i-Akbari.
- Badauni – A court historian.
- Faizi – A poet and scholar in Akbar’s court.
Painting also flourished, especially miniature paintings that showed court life, battles, and nature.
Architecture
Mughal architecture combined Persian, Islamic, and Indian styles. They built massive forts, mosques, gardens, and tombs.
Famous Monuments:
- Taj Mahal – Built by Shah Jahan in memory of his wife Mumtaz Mahal.
- Red Fort – Built in Delhi by Shah Jahan.
- Humayun’s Tomb – Early example of Mughal tomb architecture.
- Fatehpur Sikri – A planned city built by Akbar.
- Jama Masjid – One of the largest mosques in India.
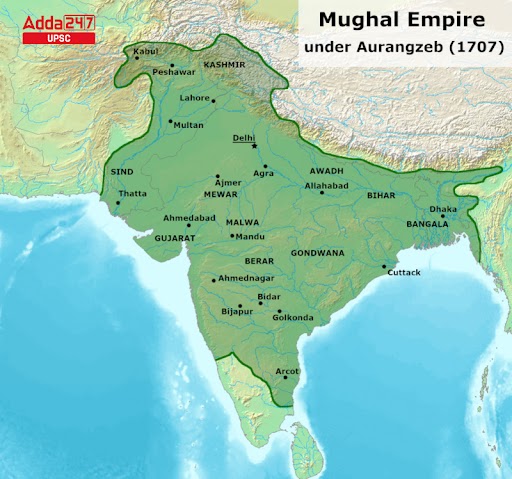
Spread of Mughal Empire
Under Akbar and Aurangzeb, the empire reached its widest extent. Akbar expanded north, west, and into central India by diplomacy and war. Aurangzeb moved into southern India, conquering Bijapur and Golconda. The empire stretched from present-day Afghanistan in the west to Bengal in the east and from Kashmir in the north to Tamil Nadu in the south.
Decline of Mughal Empire
The decline of the Mughal Empire began after Aurangzeb’s death in 1707.
Reasons for Decline:
- Weak Successors: The later emperors were not strong or capable.
- Internal Conflicts: Frequent wars between nobles weakened the empire.
- Rise of Regional Powers: The Marathas, Sikhs, and Rajputs became stronger.
- European Interference: The British East India Company gained power through trade and war.
- Revolt of 1857: The last Mughal emperor, Bahadur Shah Zafar, supported this revolt. After its failure, the British exiled him, ending the Mughal Empire in 1857.
Mughal Empire Questions asked in Railway Exams
RRB JE CBT-I (17/12/2024)
Who among the following was the ruler of Gujarat when Humayun attacked the kingdom in 1532?
A. Sikandar Shah
B. Zafar Khan Muzaffar
C. Muzaffar Shah ll
D. Bahadur Shah
Ans. D
RPF SI (09/12/2024)
Who among the following Mughal Princes allied with Malik Ambar and revolted against his father?
A Jahangir
B Akbar
C Shah Jahan
D Aurangzeb
Ans. D
RPF SI (09/12/2024)
Which of the following was the original name of Sher Shah Suri, the founder of Suri dynasty?
A Adham Khan
B Ulugh khan
C Murtaza Khan
D Farid Khan
Ans. D
RPF SI (09/12/2024)
Who among the following was appointed as the Governor of Chitor after Akbar invaded it in 1567?
A Asaf Khan
B Bairam Khan
C Adham Khan
D Maan Singh
Ans. A
RPF SI (13/12/2024)
Under the reign of which of the following Mughal Emperors did Bahadur Shah attack Chittor?
A Babur
B Humayun
C Shah Jahan
D Aurangzeb
Ans. B
RPF SI (13/12/2024)
The mother of Jahangir was a Kachhwaha princess, a daughter of Rajput ruler of ___________.
A Marwar
B Berar
C Mewar
D Amber
Ans. D
RPF Constable (10/03/2025)
When was the Battle of Kanauj fought?
A 1526
B 1540
C 1556
D 1567
Ans. B
RPF Constable (06/03/2025)
The Mughals were descendants of which clan?
A Turks
B Chaghtai Turk Mongols
C Mongols
D Afghans
Ans. B
Mughal Empire – Rulers, Fall of Empire and Complete Details PDF
Candidates can download the detailed pdf regarding Mughal Empire – Rulers, Fall of Empire, and Complete Details from the link provided below.
Click here to download Mughal Empire – Rulers, Fall of Empire, and Complete Details PDF







 Top 10 Longest Rivers in India, Largest ...
Top 10 Longest Rivers in India, Largest ...
 Longitude and Latitude of India - Defini...
Longitude and Latitude of India - Defini...
 Parliament of India Notes: Members, Func...
Parliament of India Notes: Members, Func...










